Union Membership and Native-Immigrant Labor Market Gaps | R&R at The Economic Journal
Abstract
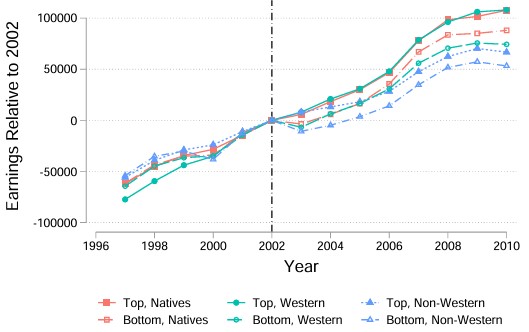
We examine if unions narrow or widen labor market gaps between natives and immigrants. We do so by combining rich Norwegian employer-employee matched register data with exogenous variation in union membership obtained through national government policies that differentially shifted the cost to workers to join a union. While union membership significantly improves the wages of natives, its positive effects diminish substantially for Western immigrants and disappear almost entirely for non-Western immigrants. The effect of unions on native wages, and the role of unions in augmenting the native-immigrant wage gap, is nonexistent in competitive labor markets while it is substantial in markets characterized by a high degree of labor concentration. This implies that unions act as a countervailing force to employer power in imperfect markets and can ameliorate the negative labor market effects of labor market concentration, but only for natives. Using unions as a means to empower workers and solve market failures caused by imperfect competition in the labor market, therefore, is likely to lead to a significant increase in societal inequality.