The Dynamics of Power in Labor Markets: Monopolistic Unions versus Monopsonistic Employers | Resubmission in preparation at Review of Economic Studies
Abstract
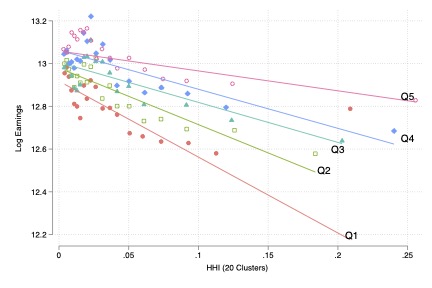
This paper brings together the literatures on employer power and employee power by studying the effect of unions on earnings, employment, and inequality across differently concentrated markets. Exploiting national government-induced changes to union due subsidies as exogenous shocks to union density, we show that high levels of unionization mitigate the negative wage and employment effects generated by imperfect competition. We also identify considerable effect heterogeneity with respect to worker types across differentially concentrated markets, and show that this has major implications for the role of unions in shaping labor market wage inequality.
Publication
Resubmission in preparation at Review of Economic Studies